工厂(Factory)模式,工厂,就是生产东西的地方,在Java设计模式中里就是生产对象的地方
说到这里我们就会想:我们一般想要一个对象,直接new一个就好了,那为什么还要多此一举的去创建一个工厂呢?
因为在某种场景下,我们需要创建多个类,而且这些类还需要针对不同的情况来创建不同的对象,这时候就需要工厂了,我们可以在工厂中根据条件来创建具体的对象
这样一来就将调用方和具体的目标类进行了解耦,调用方根本就不知道需要创建那个对象,它只是提出了条件,然后工厂就可以根据给定的条件来决定创建哪一个对象
工厂模式的实现方式分为三种:
- 简单工厂方法模式
- 工厂方法模式
- 抽象工厂模式
简单工厂方式
比如我们需要买一台手机,我们只需要告诉导购员:我需要一台Apple 11 Pro max
手机信息:
/**
* 手机信息
*/
public class MobilePhoneInfo {
// 品牌
private String brand;
// 型号
private String model;
// 价格
private BigDecimal price;
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getModel() {
return model;
}
public void setModel(String model) {
this.model = model;
}
public BigDecimal getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(BigDecimal price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MobilePhoneInfo{" +
"brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", model='" + model + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
手机接口:
/**
* 手机接口
*/
public interface MobilePhone {
MobilePhoneInfo getMobilePhoneInfo();
}
Apple 11 Pro max:
/**
* Apple 11 Pro max
*/
public class Apple11ProMax implements MobilePhone {
@Override
public MobilePhoneInfo getMobilePhoneInfo() {
MobilePhoneInfo mobilePhoneInfo = new MobilePhoneInfo();
mobilePhoneInfo.setBrand("Apple");
mobilePhoneInfo.setModel("11 Pro max");
mobilePhoneInfo.setPrice(new BigDecimal("12699.00"));
return mobilePhoneInfo;
}
}
华为mate X:
/**
* 华为mate X
*/
public class HuaWeiMateX implements MobilePhone {
@Override
public MobilePhoneInfo getMobilePhoneInfo() {
MobilePhoneInfo mobilePhoneInfo = new MobilePhoneInfo();
mobilePhoneInfo.setBrand("华为");
mobilePhoneInfo.setModel("mate X");
mobilePhoneInfo.setPrice(new BigDecimal("17500"));
return mobilePhoneInfo;
}
}
手机枚举:
/**
* 手机枚举
*/
public enum MobilePhoneType {
APPLE_11_PRO_MAX,
HUAWEI_MATE_X;
}
手机工厂:
/**
* 手机工厂
*/
public class MobilePhoneFactory {
public static MobilePhone getMobilePhone(MobilePhoneType type) {
switch (type) {
case APPLE_11_PRO_MAX:
return new Apple11ProMax();
case HUAWEI_MATE_X:
return new HuaWeiMateX();
default:
return null;
}
}
}
测试类:导购员(client)
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MobilePhone mobilePhone = MobilePhoneFactory.getMobilePhone(MobilePhoneType.APPLE_11_PRO_MAX);
System.err.println(mobilePhone.getMobilePhoneInfo().toString());
}
}
运行结果:

以上就是简单工厂方法模式,一个导购员可以给你不同的手机,你只需要跟她说你要哪个手机就行(只有一个工厂类来面向多个目标实现)
上面的做法有个很明显的缺点,那就是每当手机新品发布会的时候,我们不得不去修改工厂类的方法,使其兼容新的手机型号,这明显违背了开闭原则,所以出现了工厂方法模式
工厂方法模式
工厂方法模式是对简单工厂模式的抽象升级,将工厂这个概念抽象出来成为接口,然后针对每种目标实现类创建一个工厂实现,一对一来实现,当新增了目标实现,只要同时新增一个工厂实现即可
还是上面的那个例子:
手机信息类共用上面创建好的
手机接口:
/**
* 手机接口
*/
public interface MobilePhone {
MobilePhoneInfo getMobilePhoneInfo();
}
Apple 11 Pro max:
/**
* Apple 11 Pro max
*/
public class Apple11ProMax implements MobilePhone {
@Override
public MobilePhoneInfo getMobilePhoneInfo() {
MobilePhoneInfo mobilePhoneInfo = new MobilePhoneInfo();
mobilePhoneInfo.setBrand("Apple");
mobilePhoneInfo.setModel("11 Pro max");
mobilePhoneInfo.setPrice(new BigDecimal("12699.00"));
return mobilePhoneInfo;
}
}
华为mate X:
/**
* 华为mate X
*/
public class HuaWeiMateX implements MobilePhone {
@Override
public MobilePhoneInfo getMobilePhoneInfo() {
MobilePhoneInfo mobilePhoneInfo = new MobilePhoneInfo();
mobilePhoneInfo.setBrand("华为");
mobilePhoneInfo.setModel("mate X");
mobilePhoneInfo.setPrice(new BigDecimal("17500"));
return mobilePhoneInfo;
}
}
手机工厂:
/**
* 手机工厂
*/
public interface MobilePhoneFactory {
MobilePhone getMobilePhone();
}
Apple 11 Pro max工厂:
/**
* Apple 11 Pro max工厂
*/
public class Apple11ProMaxFactory implements MobilePhoneFactory {
@Override
public MobilePhone getMobilePhone() {
return new Apple11ProMax();
}
}
华为mate X工厂:
/**
* 华为mate X工厂
*/
public class HuaWeiMateXFactory implements MobilePhoneFactory {
@Override
public MobilePhone getMobilePhone() {
return new HuaWeiMateX();
}
}
测试类:导购员(client)
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MobilePhoneFactory mobilePhoneFactory = new HuaWeiMateXFactory();
MobilePhone mobilePhone = mobilePhoneFactory.getMobilePhone();
System.err.println(mobilePhone.getMobilePhoneInfo());
}
}
运行结果:
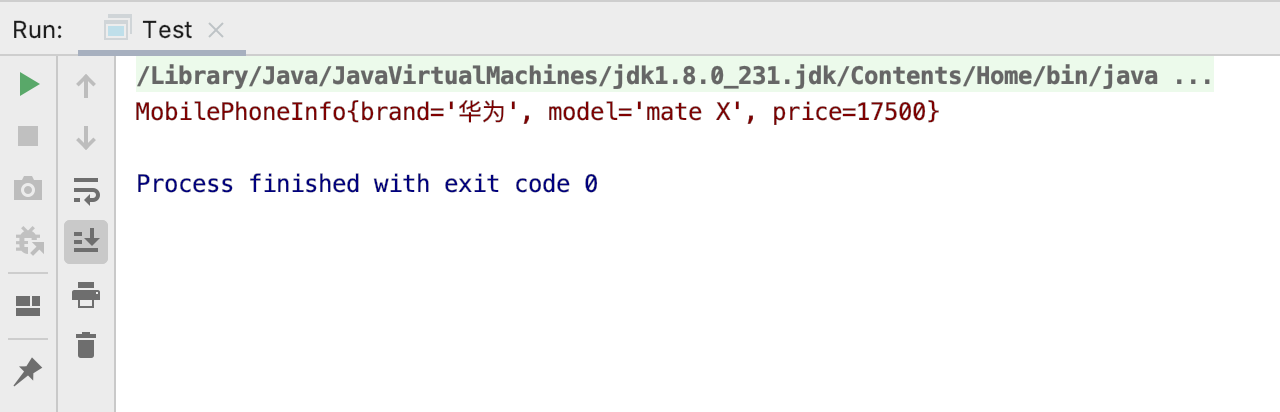
到此可以看出来,工厂方法模式的重点是在这个手机工厂接口
所以我们现在可以无限量的发布新手机,又无需改动现有的类容
你也只需要跟你的导购员说:我想要XXX手机,她就会把你想要的手机送到你面前
工厂模式在我们经常使用的MyBatis中比较常见
MyBatis中的事务模块和数据源模块都使用了工厂方法模式
以上的两种模式只适用于创建单一目标,但是想成产出组合产品类型的话就需要下面的抽象工厂模式,比如手机和耳机的组合
抽象工厂模式
手机信息:
/**
* 手机信息
*/
public class MobilePhoneInfo {
// 品牌
private String brand;
// 型号
private String model;
// 价格
private BigDecimal price;
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getModel() {
return model;
}
public void setModel(String model) {
this.model = model;
}
public BigDecimal getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(BigDecimal price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MobilePhoneInfo{" +
"brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", model='" + model + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
耳机类:
/**
* 耳机实体
*/
public class HeadsetInfo {
private String headsetName;
private String price;
public String getHeadsetName() {
return headsetName;
}
public void setHeadsetName(String headsetName) {
this.headsetName = headsetName;
}
public String getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(String price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Headset{" +
"headsetName='" + headsetName + '\'' +
", price='" + price + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
手机接口:
/**
* 手机接口
*/
public interface MobilePhone {
MobilePhoneInfo getMobilePhoneInfo();
}
耳机接口:
/**
* 耳机接口
*/
public interface Headset {
HeadsetInfo getHeadsetInfo();
}
Apple 11 Pro max:
/**
* Apple 11 Pro max
*/
public class Apple11ProMax implements MobilePhone {
@Override
public MobilePhoneInfo getMobilePhoneInfo() {
MobilePhoneInfo mobilePhoneInfo = new MobilePhoneInfo();
mobilePhoneInfo.setBrand("Apple");
mobilePhoneInfo.setModel("11 Pro max");
mobilePhoneInfo.setPrice(new BigDecimal("12699.00"));
return mobilePhoneInfo;
}
}
华为mate X:
/**
* 华为mate X
*/
public class HuaWeiMateX implements MobilePhone {
@Override
public MobilePhoneInfo getMobilePhoneInfo() {
MobilePhoneInfo mobilePhoneInfo = new MobilePhoneInfo();
mobilePhoneInfo.setBrand("华为");
mobilePhoneInfo.setModel("mate X");
mobilePhoneInfo.setPrice(new BigDecimal("17500"));
return mobilePhoneInfo;
}
}
AppleAirPods:
public class AppleAirPods implements Headset {
@Override
public HeadsetInfo getHeadsetInfo() {
HeadsetInfo headsetInfo = new HeadsetInfo();
headsetInfo.setHeadsetName("Apple Air Pods");
headsetInfo.setPrice("1299.00");
return headsetInfo;
}
}
HuaWeiFreeBuds3:
public class HuaWeiFreeBuds3 implements Headset {
@Override
public HeadsetInfo getHeadsetInfo() {
HeadsetInfo headsetInfo = new HeadsetInfo();
headsetInfo.setHeadsetName("HUAWEI FreeBuds 3");
headsetInfo.setPrice("1199.00");
return headsetInfo;
}
}
重点:手机工厂:
/**
* 手机工厂
*/
public interface MobilePhoneFactory {
MobilePhone getMobilePhone();
Headset getHeadset();
}
测试类:导购员(client)
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MobilePhoneFactory mobilePhoneFactory = new HuaWeiMateXFactory();
MobilePhone mobilePhone = mobilePhoneFactory.getMobilePhone();
Headset headset = mobilePhoneFactory.getHeadset();
System.err.println(mobilePhone.getMobilePhoneInfo());
System.err.println(headset.getHeadsetInfo());
}
}
运行结果:
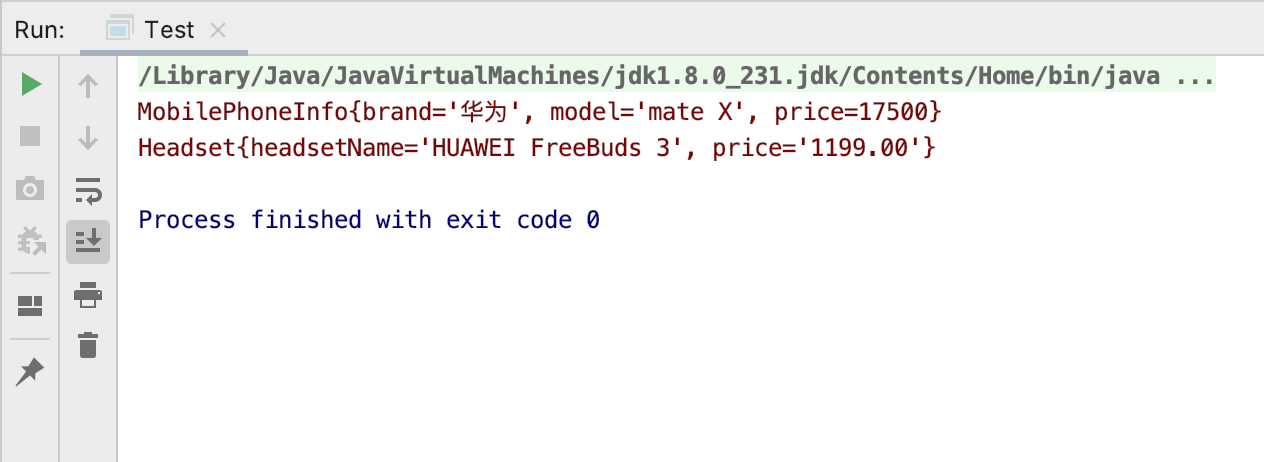
总体看来工厂模式和抽象工厂模式在实现上总体没什么太大区别,工厂模式适用于一对一的对象创建,而抽象工厂模式则是一个组合体
抽象工厂模式同工厂模式一样,没添加一种组合只需要添加对应的工厂即可,比如再加进去一个小米10
对于这一点来说,抽象工厂模式和工厂模式一样,实现了满足开闭原则,不会修改已有类
但是有一种情况,比如我们想在现有的手机耳机组合里面加售快速充电器等其他产品,那么就需要在现有所有的工厂和工厂接口上都统一进行修改